Extending CSE Research
Researching the impact of CSEs to transportation

As we see from the previous blogpost, Viktor Grebennikov’s flying platform is described in detail. However, we didn’t spend much time analyzing the platform. Prior to a more in-depth study of the platform, a reexamination of the Cavity Structure Effect (CFE) is necessary. Also from the previous blogpost is the article “Cavity Structural Effect” by Ville Piippola:
According to B. N. Rodimov (1976, as cited by Frolov, 2001) the walls of multi cavity structures can be considered as the boundaries of the potential electron’s box. The group movement of electrons leads to a system of standing de Broglie waves, which have classic frequencies.
The classic frequencies are f = nh/4mL2, where n is an integer number, L is the circumference of cavity in centimeters, and m is the effective mass of the electron. As an example, the classic frequency for 4.9 mm (side to side) diameter honey bee comb cell is calculated. The effective mass of an electron in beeswax is a bit hard to calculate, and therefore, in the calculation the free electron rest mass is used.
f = 1 · 6.626 · 10-34kgm2s-2 / 4 · 9.11 · 10-31kg · (1.7cm)2= 0.63 Hz
Further, Zolotariov gives a formula for the locations of de Broglie wave maximums: D = 2L(N+1)2K, where L is the circumference of the tube, N is the harmonic number of the wave, and K is the number of the anti-node/maximum.
Relation of CSEs to transportation
The importance of understanding CSEs is imperative for utilizing them as a source for motion. Also in the previous blogpost, the article from pdfcoffee was referred to. This explains Viktor Grebennikov’s floating platform and it mentions the role of leptons. Theoretical physics is an interesting field of science: it’s filled with theories.
CATTCC subscribes to a theory of particle mass that postulates all mass travels a specific path, a unified direction. This theory minimizes many other theories relating to how particles react. The path of particle movement is foundational to the explanation of gravity that CATTCC subscribes to. In regards to leptons, gravitons, and even aether, matter is traveling at a consistent frequency as the speed of light; explained by Einstein’s theory of relativity.
The discovery of particle mass by bombardment of accelerating particles, smashing them into another particle and then naming the offshoot remnant, is not a natural occurrence. The flow of particles traveling at light speed through the universe is more consistent to natural occurrence. The point here is to identify aether as the presents of relativity; it is the movement of light speed motion. Leptons and gravitons are the ambiguous particles that account for wrecked, and perhaps stray particles; inconsistence with nature’s consistence flow. This is to say that nature is consistent with natural flow instead of intruding particle bombardments. CERN and other particle accelerator labs are similar to being on a train and throwing a rock through the train window and taking a picture of the braking glass to see what’s outside. Perspective is a variable.
All this rambling to say that in context to the term ‘leptons’ used synonymously with aether; use of the term aether is more consistent in accuracy to relativity. An understanding of deBroglie waves can be found in Wikipedia but, is redirected as an explanation of Matter wave:
Matter waves are a central part of the theory of quantum mechanics, being half of wave–particle duality. All matter exhibits wave-like behavior. For example, a beam of electrons can be diffracted just like a beam of light or a water wave.
The concept that matter behaves like a wave was proposed by French physicist Louis de Broglie (/dəˈbrɔɪ/) in 1924, and so matter waves are also known as de Broglie waves.
The de Broglie wavelength is the wavelength, λ, associated with a particle with momentum p through the Planck constant, h:
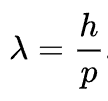
Further in Wikipedia’s definition, is the following:
Collective matter waves
See also: List of quasiparticles
Other classes of matter waves involve more than one particle, so are called collective waves and are often quasiparticles. Many of these occur in solids – see Ashcroft and Mermin. Examples include:
- In solids, an electron quasiparticle is an electron where interactions with other electrons in the solid have been included. An electron quasiparticle has the same charge and spin as a "normal" (elementary particle) electron and, like a normal electron, it is a fermion. However, its effective mass can differ substantially from that of a normal electron. Its electric field is also modified, as a result of electric field screening.
- A hole is a quasiparticle which can be thought of as a vacancy of an electron in a state; it is most commonly used in the context of empty states in the valence band of a semiconductor. A hole has the opposite charge of an electron.
- A polaron is a quasiparticle where an electron interacts with the polarization of nearby atoms.
- An exciton is an electron and hole pair which are bound together.
- A Cooper pair is two electrons bound together so they behave as a single matter wave.
As a synopsis, in looking at Matter waves, comes this jewel: a hole has the opposite charge of an electron. Hence; the vibration of polarization. This is pertinent to CSEs. And now, taking all this information about levitation and building a transportation device.
To the research of Viktor Grebennikov’s levitating platform, the previous blogpost provided a step-by-step look into his device. In looking to define rebuilding Grebennikov’s platform there are many questions. Our study continues, a little at a time. Deciphering this is like a puzzle.
Two bolt heads can also be seen on the photographs, approximately in the center of each platform halves. This is a bonding of the distribution mechanism, which transfers effort from the “distributors” to a fan opening device.
Since there are no photographs available, the description becomes the visual palette. There are two platform sections, folded to make a single mechanism wherein the distribution of effect is enacted.
Regarding the use of the term ‘fan’, after much deliberating thought, this reference is a hand fan shape, rather than a rotary electric motor fan. A fanning action consists of nine plates over the two sections.
Each fan consists of nine plates. In order to make them strong, the plates are made of sheet metal. Micro-nets are stuck from the upper surface of each plate. On the one hand, the metal does not prevent nets from operating because the effect of cavitary structures cannot be screened and, on the other hand, protects them from mechanical influences such as influence of grass during landing. Holes in the plates, which can be seen, are not related to micro-cells. They are made only for lightening the metal plates’ weight. Do you see that it is difficult for Grebennikov to hold even a lightened version of his platform?
What is the structure
A micro-net is the stacking of CSEs. This structure is undefined. The several blogposts regarding chitin and crystal polymerizations refer to this type of CSEs.
Antigravity effect (created due to the effect of cavitary structures) is produced by the cells but they need “fuel” in order to work with maximal efficiency.
Roughly speaking, the effect of cavitary structures works the following way: any material consists of particles vibrating by its own frequency (read Tesla’s cosmology, works of John Keely, Thomas Henry Morey, Wilhelm Reich and others). Due to such internal atomic vibrations, a stationary wave exists in the environment, around any object (and further, discrete “reflections” or maximums of such a wave).
This process is known as resonance. It can be energized by an electromagnetic pulsation.
Thus, a frequency and length of such vibration are unique for any material (according to Grebennikov, this is a “reflection of de Broglie waves). If we make a cavity, its walls will begin to “radiate” towards each other or under some angles. If a right size of such a cell will be found, waves’ maximums will sum up and a field will be strengthened in the given point of space (field antinode).
So, let us make conclusions. First, as many as possible surfaces are necessary for one cell (it may seem strange but a polygon with maximal quantity of sides, which can be used for filling a plane without gaps and fractally is a hexagon). Second, the less the size of each cell, the more quantity of surfaces, which we can have with the same volume. The more cells and, accordingly, the more surfaces, the stronger the effect of cavitary structures. Let us remark more that size of one cell is not arbitrary but divisible by wave “reflections” (maximums’ position), which, in their turn, depend on a used material. Wave “reflections” can be far from the surface as well as very close to it. Closer ones have stronger power.
Further analysis is needed to build a levitating transportation device. This study will continue.



