Schumann Resonance
How do Schumann Resonances relate to a new mode of transportation
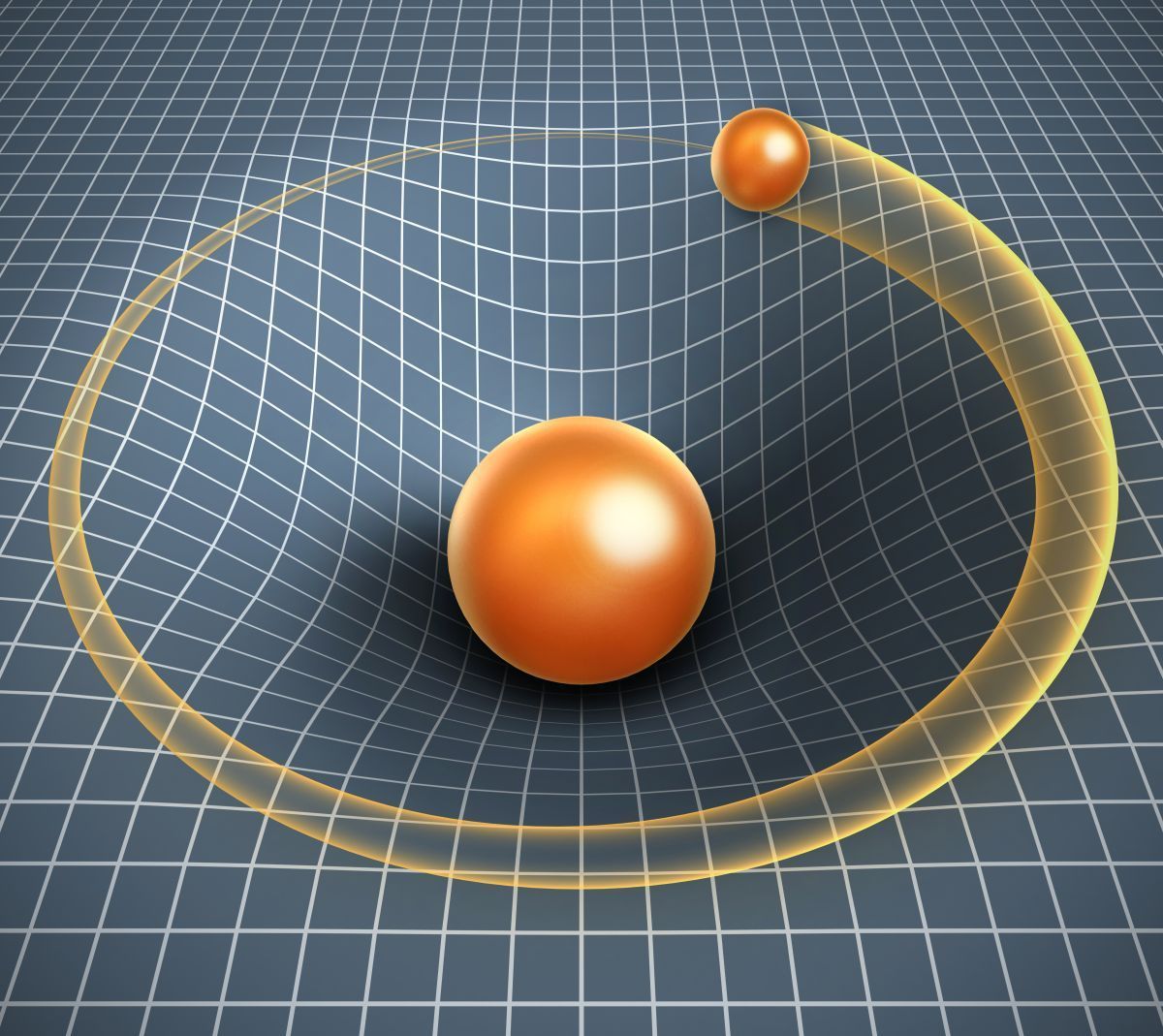
The Schumann resonances are identified as a series of low frequency electromagnetic waves in Earth’s ionosphere. This series of electromagnetic spectrum range from 3Hz to peaks up to 60Hz. The Schumann resonances were discovered by physicist Winfried Otto Schumann in 1952.
Wikipedia describes the Schumann frequency as:
The Schumann resonances (SR) are a set of spectrum peaks in the extremely low frequency portion of the Earth's electromagnetic field spectrum. Schumann resonances are global electromagnetic resonances, generated and excited by lightning discharges in the cavity formed by the Earth's surface and the ionosphere.
Schumann resonances occur because the space between the surface of the Earth and the conductive ionosphere acts as a closed, although variable-sized waveguide. The limited dimensions of the Earth cause this waveguide to act as a resonant cavity for electromagnetic waves in the extremely low frequency band. The cavity is naturally excited by electric currents in lightning.
Effects on Schumann resonances have been reported following geomagnetic and ionospheric disturbances. More recently, discrete Schumann resonance excitation has been linked to transient luminous events — sprites, ELVES, jets, and other upper-atmospheric lightning.
Do the Schumann resonances have relevance to Grennikov’s Cavity Structures Effects (CSEs)? In a remarkable new study by Vitor Matheus Izoldi Nogueira, the Earth’s magnetosphere does have an effect to spiders movement.
The basis for the theory of Schumann resonances are defined by Wikipedia as:
Lightning discharges are considered to be the primary natural source of Schumann resonance excitation; lightning channels behave like huge antennas that radiate electromagnetic energy at frequencies below about 100 kHz.[23] These signals are very weak at large distances from the lightning source, but the Earth–ionosphere waveguide behaves like a resonator at extremely low frequency and amplifies the spectral signals from lightning at the resonance frequencies.[23]
In an ideal cavity, the resonant frequency of the n-th mode fn is determined by the Earth radius n and the speed of light c
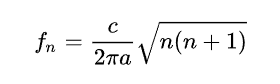
The real Earth–ionosphere waveguide is not a perfect electromagnetic resonant cavity. Losses due to finite ionosphere electrical conductivity lower the propagation speed of electromagnetic signals in the cavity, resulting in a resonance frequency that is lower than would be expected in an ideal case, and the observed peaks are wide. In addition, there are a number of horizontal asymmetries—day-night difference in the height of the ionosphere, latitudinal changes in the Earth's magnetic field, sudden ionospheric disturbances, polar cap absorption, variation in the Earth radius of ± 11 km from equator to geographic poles, etc. that produce other effects in the Schumann resonance power spectra.
The bigger question relates to the relationship of Earth’s magnetosphere, de Broglie waves, the ionosphere, electromagnetism and its potential to affect a levitating transportation device.
The other related topic for study is Earth’s magnetic field. In the British Geological Survey (BGS) is a thorough examination:
The Earth's magnetic field is generated in the fluid outer core by a self-exciting dynamo process. Electrical currents flowing in the slowly moving molten iron generate the magnetic field. In addition to sources in the Earth's core the magnetic field observable at the Earth's surface has sources in the crust and in the ionosphere and magnetosphere. The geomagnetic field varies on a range of scales and a description of these variations is now made, in the order low frequency to high frequency variations, in both the space and time domains. The final section describes how the Earth's magnetic field can be both a tool and a hazard to the modern world. First of all, however, methods of observing the magnetic field are described.
The electromagnetic fields which surround the planet are astounding. NASA describes Earth’s magnetosphere as:
Earth's magnetosphere is part of a dynamic, interconnected system that responds to solar, planetary, and interstellar conditions. It is generated by the convective motion of charged, molten iron, far below the surface in Earth's outer core. Constant bombardment by the solar wind compresses the sun-facing side of our magnetic field. The sun-facing side, or dayside, extends a distance of about six to 10 times the radius of the Earth. The side of the magnetosphere facing away from the sun - the nightside - stretches out into an immense magnetotail, which fluctuates in length and can measure hundreds of Earth radii, far past the moon's orbit at 60 Earth radii.
To consider a levitating transportation device having the ability to interact with Earth’s magnetosphere, places that possibility in the realm of a radio signal being able to be transmitted and received at a different location. De Broglie waves consist of matter waves having the function of travel. The importance of Einstein’s theory of relativity proposing that the Milky Way Galaxy traveling at light speed, holds the postulation that matter is traveling. Electromagnetic waves carry their motion in the similar manner that matter moves through the universe. A levitating device should be able to utilize the compression of a void (CSE) with that interaction.
As an explanation of the ionosphere, let’s ask the question: what is an ion?
An ion is a charged atom or molecule. It is charged because the number of electrons do not equal the number of protons in the atom or molecule. An atom can acquire a positive charge or a negative charge depending on whether the number of electrons in an atom is greater or less then the number of protons in the atom.
When an atom is attracted to another atom because it has an unequal number of electrons and protons, the atom is called an ION. If the atom has more electrons than protons, it is a negative ion, or ANION. If it has more protons than electrons, it is a positive ion.
This activity is similar to electromagnetism. Ion interaction without the presents of ferrous elements is electrogravitics:
What is electrogravitics? As to relevance for a discussion about electrogravitics it delves into theoretical physics fundamentals. Electrogravitics is proposed as a foundational component to the theory of particle mass composition. Electrogravitics is similar to electromagnetics but identifies gravity as the component to subatomic electric fields. This leads to speculation that gravity is a subatomic process rather than a product of mass. With this perspective, electrogravitics holds more validation than electromagnetics as the source of particle charge.
Inasmuch as electromagnetics is the current dictate considered as the primary source of particle charge, it is the supposition of a new theory for gravity that electrogravitics is responsible for what is referred to as electric charge in subatomic matter.
This information is more research in the study to find an answer in discovery for developing an new mode of transportation.



